A router connects different networks with each other to share packets of data. To route a packet, a router needs to know:
- Destination IP addresses
- Learning sources
- Possible routes to the destination
- Best route to the destination
- Verify and maintain the routing information
Routers must learn the destinations that are not directly connected through IP routing. Routing uses a route that a network routing protocol adjusts automatically for topology or traffic changes. Routing protocols are used between routers to determine paths and maintain routing table. Once the path is determined a router can route a routed protocol such as IP while RIP, the Routing Information Protocol is an example of routing protocol.
The other examples of routing protocols are as follows: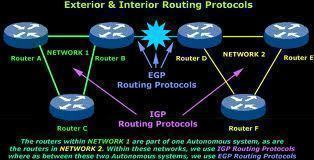

- Destination IP Addresses
- Learning sources
- Possible routes to the destination
- Best route to the destination
- Verify and maintain the routing information
- BGP: Border Gateway Protocol
- EGP: Exterior Gateway Protocol
- EIGRP: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
- IGRP: Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
- IS-IS: ISO IS-IS
- OSPF: Open Shortest Path First
There are three classes of routing protocol:
- Distance Vector Routing Protocol such as RIP and IGRP
- Link State Routing Protocol such as OSPF
- Hybrid Routing Protocol such as EIGRP
Information on RIP, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP Routing Protocol
The Routing Information Protocol is an open standard based Distance-Vector routing protocol. It comes on two versions RIP v.1 and RIP v.2.
The Open Shortest Path First is an example of Link State routing protocol that supports variable length subnet masking and discontiguous subnets.
The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol is an enhanced Distance Vector routing protocol. It is also known as hybrid routing protocols that shares the attributes of both Distance Vector and Link State. It is a scalable routing protocol, even the largest EIGRP installation in the world network is running successfully with no EIGRP offset.
EIGRP vs IGRP
The Border Gateway Protocol is an exterior gateway protocol that provides inter-autonomous system routing. It is the protocol of the internet. BGP operates in one of two modes: internal BGP and external BGP. BGP path attributes fall into 4 separate categories:
RIP: Followings are some important features of RIP:
- RIP supports Bellman and Ford algorithm.
- RIP v.1 uses hop count as a metric while RIP v2 routing protocol metric is also hop count.
- The maximum hop counts for both are 15.
- RIP v.1 features the use of broadcast updates while RIP v.2 features the use of multicast routing updates.
- RIP v.1 is a classful routing protocol that supports FLSM while RIP v.2 is a classless routing protocol that supports VLSM.
- The administrative distance of RIP is 120.RIP supports equal metric load balancing. OSPF: Followings are some important features of OSPF:
- OSPF advertise a large amount of topological information about the network includes what every metric is for every link.
- OSPF uses Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to calculate the metric.
- Using OSPF, routers perform CPU intensive data computations.
- OSPF discovers neighbours before exchanging routing information.
- The administrative distance of OSPF is 110.
- OSPF is a classless routing protocol that supports VLSM and CIDR.
- OSPF supports equal metric load balancing.
- The metric of OSPF is cost.EIGRP: EIGRP possesses the following features:
- It supports Variable Length Subnet Mask.
- It does not send a complete copy of its routing table to neighbours on a periodic basis.
- It can be enabled for IP as well as IPX and AppleTalk are also used as EIGRP protocols to connect EIGRP networks.
- It automatically redistributes routes with IGRP processes define in the same autonomous system.
- It performs same metric accumulation as IGRP.
- It creates topology table in addition to routing table for largest EIGRP network build.
- It converges quickly.
- Bandwidh, delay, load, reliability and MTU are used for calculating EIGRP routing metric.
- It uses dual algorithm.
- The administrative distance of EIGRP is 90.
- It is the Cisco proprietary routing protocol along with IGRP.
- It supports unequal metric load balancing by using “variance” command.The EIGRP is supposed the second generation of IGRP but it has some differences as well as some similarities. The comparison of EIGRP over IGRP is as follows:
- Both are Cisco Proprietary protocols.
- Both have same logic for equal cost paths.
- IGRP and EIGRP path selection is based on Bandwidth/Delay metric. Using some EIGRP commands maximum bandwidth can be changed as required while in IGRP it cannot be changed.
- Both have same metric accumulation, if divide the EIGRP metric by 256.
- EIGRP has fast convergence time while IGRP has a slow convergence time.
- EIGRP discovers neighbour before exchanging routing information while IGRP does not.
- IGRP sends full routing table during update while EIGRP does not, that’s why in EIGRP split horizon issue does not come.
- IGRP requires Distance Vector loop avoidance features while EIGRP does not.
- EIGRP uses Dual algorithm while IGRP uses Bellman and Ford algorithm.
- IGRP send periodic routing updates every 90 seconds while EIGRP send triggered change-based updates when there is a topology change has been occurred.BGP:
- Well-known Mandatory
- Well-known Discretionary
- Optional Transitive
- Optional non-transitiveBGP path attribute usages are as follows:
- ORIGIN (BGP 4 Type Code 1)
- AS_PATH (BGP 4 Type Code 2)
- NEXT_HOP (BGP 4 Type Code 3)
- MULTI_EXIT_DISC (BGP 4 Type Code 4)
- LOGICAL_PREFERENCE (BGP 4 Type Code 5)
- AUTOMIC_AGGREGATE (BGP 4 Type Code 6)
- AGGREGATOR (BGP 4 Type Code 7)
Related Articles



0 comments:
Post a Comment