What is Subnet Mask?
Most of the users did not know about subnet masks that what is a subnet mask and what is the purpose of a subnet mask. The patent definition of a subnet mask is that a subnet mask is a 32-bit doted decimal based number that determines how an ip address on bitwise bases is split in to network and host portions. The two fundamental rules if subnetting are as follow:
- If a bit in a subnet mask has a value of one, then the bit is part of the network prefix in the corresponding ip address.
- If a bit in a subnet mask has a value of zero, than the bit is part of the host suffix in the corresponding ip address.
Default Subnet Mask
When applying the two rules of subnetting to classful addresses, the default subnet mask for different classes of the ip addresses are:
- Class A = 255.0.0.0
- Class B = 255.255.0.0
- Class C = 255.255.255.0
Where 255 represents network prefix and 0 represents host suffix. In the above table 255.0.0.0 is a standard class A subnet mask, since the first bit are all once (network) and the last three bites are all zeros (host). When this subnet mask is applied to a class A network, no subnetting is performed.
How to Find Out Your Subnet Mask?
H5 { margin-bottom: 0.21cm }
In a network environment where all the network devices are physically connected with each other and the ip settings including the subnet masks of all the devices have been configured. To view that what is my subnet mask you have to execute the following commands on the command line interfaces of different Operating System:
This is the DOS command that executes the ip address and subnet mask of your computer that used any version of Microsoft Windows Operating System such as Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
This is the DOS command that executes the list of the ip address and subnet masks including some other network relating information of your Windows based computer.
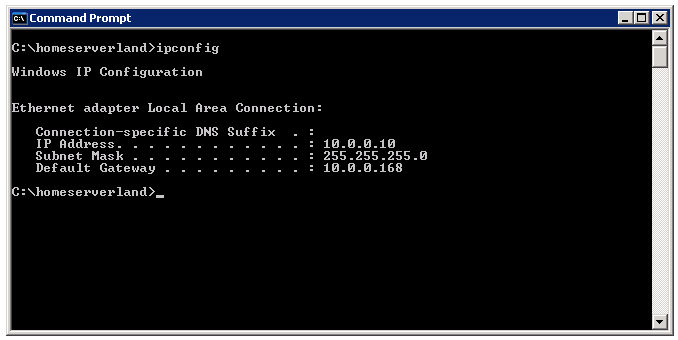
This is the case-sensitive Shell command that executes all the ip configurations including subnet mask of your Linux computer.
This is the command used to view the ip configuration settings including the ip address and subnet mask of the Cisco Catalyst 1900 Switch.
This is the command used for viewing the ip addresses and subnet masks along with other interface configurations of the existing interface in the Cisco Catalyst 2950 Switch and most of the routers such as Cisco 2500 Router and Cisco 2600 Router.
- ipconfig
- Ipconfig/all
- ifconfig
- Show ip
- Show ip interface
How to Change Subnet Mask?
The subnet mask is a value that basically differentiates the network and host portion of your networking device. If you can change the subnet mask of your computer for some purpose you can change by two different methods either by using graphical tools or by using command line interface.
Following are the details of both the methods in the Microsoft Windows Operating System:
- In the properties tab of Local Area Connection you should have to select TCP/IP and click the properties tab of TCP/IP. Click once on the field of subnet mask and delete the old subnet mask, then configured the new subnet mask and click on OK tab and then click OK. Check the new subnet mask with the command "ipconfig".
- You should have to execute the command "set address local static ip address subnet mask" in the netsh interface ip> mode of your Microsoft Windows computer.
Variable Length Subnet Mask
There are two types of subnetted environment such as Fixed Length Subnet Mask (FLSM) and Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM). The FLSM environment supports multiple subnets of same number of host using one subnet mask in all the subnets while Variable Length Subnet Mask supports multiple subnets of different length and different number of hosts using different subnet masks i different subnets. The selection of routing protocol also determines whether you are stuck with a FLSM environment or whether you can deploy VLSM. RIP v.1 and IGRP support only FLSM while RIP v.2, EIGRP, OSPF and IS- IS support VLSM.
A FLSM (Fixed Length Subnet Mask) network environment is too inflexible when you require various types of subnet mask for the same network address. For example, consider a large organization with a single class B address of 172.16.0.0. Its headquarters site is made up of four subnets with 250 hosts on each subnet. The same organization has ten regional offices, with a single LAN with less then 60 hosts each. Finally, this organization has 500 field offices. Each field office has a single segment with less then five hosts each. Which of the following subnet mask is best for this organization?
- A 24 bit subnet mask yielding 254 subnets with each subnet yields 254 valid host addresses each (255.255.255.0).
- A 26 bit subnet mask yielding 1022 subnets with each subnet yields 62 valid host addresses each (255.255.255.192).
- A 29 bit subnet mask yielding 8190 subnets with each subnet yields 6 valid host addresses each (255.255.255.248).
The answer is either all of them or none of them individually. The 24 bit subnet mask can be deployed at then central site. The 26 bit subnet mask can be deployed at the branch offices while the 29 bit mask can be deployed at the field offices. However, a FLSM environment can not accommodate deploying all of these different length subnet masks for a single classful network prefix.
Related Articles



0 comments:
Post a Comment