Understanding the Cisco Three-Layer Hierarchical Model
Hierachical network design helps us to make networks more reliable and predictable. Level by level design help to understand networking factions easily like, we can use tools like access lists at specific level and can avoid them from others.
Cisco layer model consist of the following three layers.
- The Core layer
- The Distribution layer
- The Access layer
Each layer plays a role and specific responsibilities are assigned to these three logical layers. These layers are same like the network layers of OSI reference model.
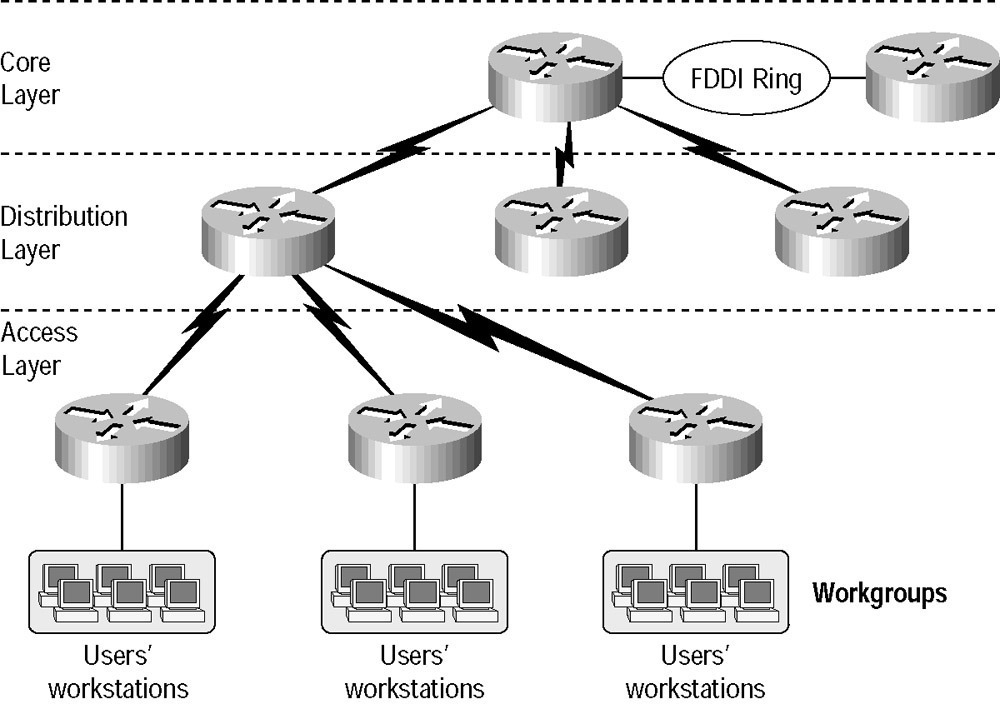
The seven layers in OSI modeldescribe some functions but not protocols. One protocol is could be mapped to more than one layers and more than one protocol can communicate with one layer. In the same way, using Cisco model we can build physical implementations of using hierarchical networks implementations. We can use many devices in a single layer and we can also use single device to perform functions at two layers.
Here is the detailed explanation of these layers.
Core Layer
Core layer is know as core of network as it is on the top of the network and it is responsible to transfer heavy amount of traffic in reliable and quick manner. Objective of core layer is to speed up the network traffic as much as possible. Traffic at core layer is common for most of users and user data is transported to distribution layers which forwards requests if it is required. If core layer is affected by a failure, every user is affected on network. Fault tolerance is main thing to consider on this layer.
The main responsibility of core layer is to see heavy traffic, so speed and traffic issues are concerned at this layer. What are functions of core layer not do the following things.
The main responsibility of core layer is to see heavy traffic, so speed and traffic issues are concerned at this layer. What are functions of core layer not do the following things.
- Protect the network from slowing down the traffic, use of access lists, routing between different Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) and Packet Filtering.
- Protect network from workgroup access support.
- Don't expand core as network grows. Try to overcome performance issue by adding routers and prefer to upgrade devices over expansion.
However while designing core, we want to do the following things.
- Design the core by using data link technologies which provides speed and redundancy like FDDI, Fast Ethernet and ATM.
- Prefer to select protocols with low convergence time and fast redundant link connectivity.
Distribution Layer
It is also known as workgroup layer and it is called communication point between access and core layer. Basic function of distribution layer is routing, filtering and WAN access and find out the method by which packets can access the core. This layer must find out the fastest mechanism to handle network operations like how to handling and forwarding a file to server on request. After finding best path, distribution layer forward request towards core layer and then to the right service. Policy implementation is done on distribution layer and you can exercise flexibility defining network operations.
Here are the functions which should be done at distribution layer.
- Implementations of access lists for filtering interesting traffic and blocking uninteresting traffic.
- Security and network policy implementation containing address translation and firewalls.
- Static routing redistribution
- Enabling routing between all VLANs
- Defining broadcast and multicast domains
The Access Layer
User and workgroup access to network and resources is defined at access layer and this layer is also known as desktop layer.
Here are some functions of access layers.
- Manage access control and policy
- Create separate collision domains
- Connectivity of workgroup through distribution layer
DDR (Double Data Rate) and Ethernet switching technology are mainly used in access layer with Static routing.
Related Articles
- Cisco Three Layer Hierarchical Model vs OSI Model
- Understanding Switching
- Application Layer
- Network Layer
- Data Link Layer



0 comments:
Post a Comment