The Windows Registry is a database designed to store options and various hardware and software configuration settings on MS Windows Operating Systems (OS's). Since the registry was first introduced in Windows 3.1, it has grown from storing COM-based component configuration information to management of settings for all of the programs installed on the computer. Today, the registry contains settings for the OS kernel, user interface preferences, device drivers, and other services in order to help the computer performance with as fast as possible. A common task for Windows computer users is how to access the registry on their computer.
What Are Some Common Registry Problems?
Registry issues can arise on your computer for a number of reasons. Some of these include orphaned registry entries that result from removing old programs, computer malware or spyware infection, and through obsolete entries created from operating system updates or new hardware or software installations. Specifically, common problems include: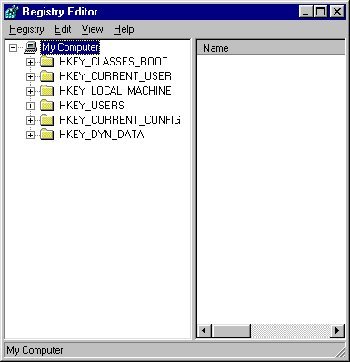

- Corrupted COM objects
- Unused desktop short cuts or start menu items.
- Software locations
- Unused files and residual registry entries
- Undesired drivers
- Remnants from removed software programs and components
- Scandisk or Checkdisk file fragments
- Shortcut files that no longer point to installed programs
- Obsolete folders and shared DLL files.
- File associations and extensions
How to Access the Registry
Accessing the registry is a straightforward process on a Windows computer. The REGEDIT application is the built-in tool installed on the MS Windows operating system since the registry database was adopted with the Windows 3.1 installation. In order to access the registry, you have to open the REGEDIT program from the DOS console.
Step 1 – Select the “Start” and “Run” menu options.
Step 2 – Enter “REGEDIT” at the DOS console prompt or in the search text field depending on the version of Windows installed on your computer.
Step 3 – Click the “Ok” menu button if queried to continue with opening the registry editor.
Step 4 – Choose the “Edit” and “Find” menu options on the REGEDIT file menu to open the search field to locate registry entries on your computer.
Step 5 - Enter the filename or descriptive word you intend to use for locating the desired registry entry.
Step 6 – Choose the “Next” menu button and view the results on the subsequent screen. Click the “F3” function key in order to see multi-page results from the registry query.
Step 2 – Enter “REGEDIT” at the DOS console prompt or in the search text field depending on the version of Windows installed on your computer.
Step 3 – Click the “Ok” menu button if queried to continue with opening the registry editor.
Step 4 – Choose the “Edit” and “Find” menu options on the REGEDIT file menu to open the search field to locate registry entries on your computer.
Step 5 - Enter the filename or descriptive word you intend to use for locating the desired registry entry.
Step 6 – Choose the “Next” menu button and view the results on the subsequent screen. Click the “F3” function key in order to see multi-page results from the registry query.
Exercising Caution While Accessing the Registry
Most computer users need to be careful while accessing and modifying the computer's registry. Making inadvertent mistakes while editing the system registry can result in catastrophic errors occurring in the Windows operating system. Before accessing the registry, making a backup of the entries you intend on modifying is critical to guarding against errors.
Steps to Backup the Registry
Step 1 – With REGEDIT open, select the “Export Registry Files” from the REGEDIT file menu.
Step 2 – Choose the folder to save the backup file and select a file name for the backup.
Step 3 – Click the “Save” menu button and the backup file will be saved to your computer.
Step 2 – Choose the folder to save the backup file and select a file name for the backup.
Step 3 – Click the “Save” menu button and the backup file will be saved to your computer.
Related Articles
- How to Edit the Registry
- How to Clean the Registry
- Windows Registry Hacks
- How to Auto-Hide the Taskbar with the Registry
- Free Registry Cleaners



0 comments:
Post a Comment